Introduction to CSS
- Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is a style sheet language used for describing the presentation of a document written in a markup language like HTML.
- CSS is a cornerstone technology of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and JavaScript.
- CSS was Developed by Hakon Wium Lie of MIT in 1995. In 1996, level 1 of CSS was published, level 2 comes in 1998 and level 3 ( CSS3) in 2009 with HTML5.
- CSS describes how elements should be rendered on screen, on paper, in speech, or on other media.
- CSS saves a lot of work. It can control the layout of multiple web pages all at once
- With CSS, it is easier to build a website, as css can style whole website using one single css file.
- CSS handles the look and feel part of a web page.
- Using CSS, you can control the color of the text, the style of fonts, the spacing between paragraphs, how columns are sized and laid out, what background images or colors are used, layout designs, variations in display for different devices and screen sizes as well as a variety of other effects.
CSS Syntax
- A CSS rule-set consists of a selector and a declaration block:
- The selector points to the HTML element you want to style.
- The declaration block contains one or more declarations separated by semicolons.
- Inside declaration block, property:value pair is used.
- Colon : is used to separate property and value.
- To add next property value pair, use ; semi-colon.
- CSS Syntax is not case-sensitive, but prefer lowercase.
CSS Property and Value
- Each declaration includes a CSS property name and a value, separated by a colon.
- Multiple CSS declarations are separated with semicolons, and declaration blocks are surrounded by curly braces.
- CSS provides variety of properties for styling and positioning the HTML web pages.
Example: font, border, text-decoration, background, position, padding, margins, etc..
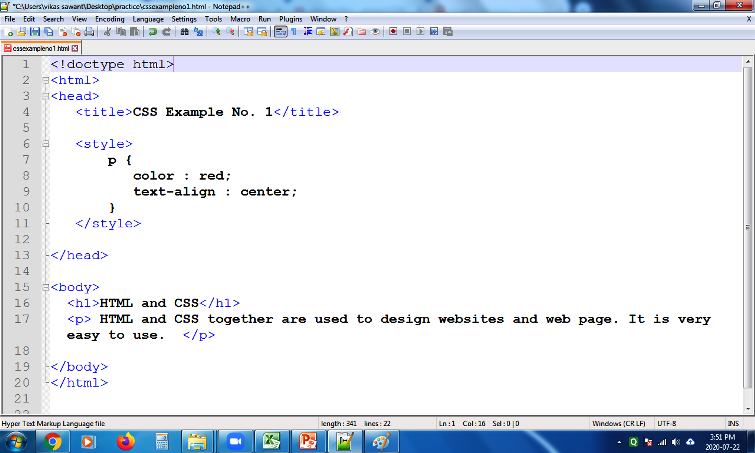
CSS Styles are usually written inside <style> element under Head Section. This way of styling is Internal CSS.
Applying CSS in HTML
You can do in three ways:-
- Create a separate CSS file containing style property-value pairs and link it with <link> tag.
- Write CSS property-value pairs in the web page inside <style> tags
- Write CSS property-value pairs in the HTML element starting tag using STYLE attribute
There are three ways of inserting a style sheet:
- External CSS - Create a separate CSS file containing style property-value pairs.
- Internal CSS - Write CSS property-value pairs in the web page inside <style> tags.
- Inline CSS - Write CSS property-value pairs in the HTML element’s Starting tag using STYLE attribute.
INLINE CSS
Inline CSS
- Inline CSS allows you to apply a unique style to one HTML element at a time.
- You assign CSS to a specific HTML element by using the style attribute with any CSS properties defined within it.
- The style attribute is written in the starting tag of a HTML element
When to use Inline CSS?
- Inline styles in CSS could be useful for previewing changes instantly or adding CSS rules to only one or two elements.
- Tip: use of inline CSS is not a recommendation. Combining CSS and HTML leads to messy code.
- Additionally, inline styles method is difficult to update.
- Note: Inline CSS styles will always override style properties determined in internal or external style sheets.

Internal CSS or Embedded CSS
- Internal CSS is used to apply styles on a single document or page.
- It is written inside the <style> tags within head section.
- Styling changes apply to every specific element found in the file.
External CSS
- An external stylesheet is used when you want to apply one style to whole website (multiple web pages)
- The styles are written in a separate file with .css extension.
- The stylesheet files are linked using the <link> tag which should be placed in the head section of an HTML page
- Using External Stylesheets, You can apply same styles to multiple web pages.
External CSS - <link> tag
The <link> tag defines the relationship between the current document and an external resource.
Attributes in the link tag:
- rel - Specifies the relationship between the current document and the linked document. It takes the value “stylesheet”.
- href - Specifies the location of the linked external stylesheet.
- Type - Specifies the media typed of the linked document. Value: “text/css”
We can have all the three methods applied to a web page. If same CSS property is defined for an element in Internal, External as well as Inline, then Inline CSS has the highest priority, then comes Internal/Embedded followed by External CSS which has the least priority.
Which style has highest priority?
What style will be used when there is more than one style specified for an HTML element?
All the styles in a page will "cascade" into a new "virtual" style sheet by the following rules, where number one has the highest priority:
Inline style (inside an HTML element)
Internal style sheets and External (in the head section)
Browser default
So, an inline style has the highest priority, and will override external and internal styles and browser defaults.
Use <link> tag in the head section of all these web pages.
<link rel=“stylesheet” type=“text/css” href=“style.css”>
CSS Homework
Create a web page with a heading and a paragraph. Using CSS apply the following:
- Apply a background color to the webpage.
- Change the color of heading to blue and alignment center.
- Change the font of paragraph to ‘Verdana’ and font size to 20px.